Welcome to another beginner-friendly guide to JavaScript! Today, we're diving into the world of conditional statements. Don't worry if you're not sure what that means – we'll break it down step by step.
What are Conditional Statements?
Conditional statements are like the "if this, then that" rules in JavaScript. They allow your program to make decisions based on certain conditions. We have two main types of conditional statements: if...else and switch.
if...else Statement
The if...else statement is like making a choice in everyday life. Let's break it down:
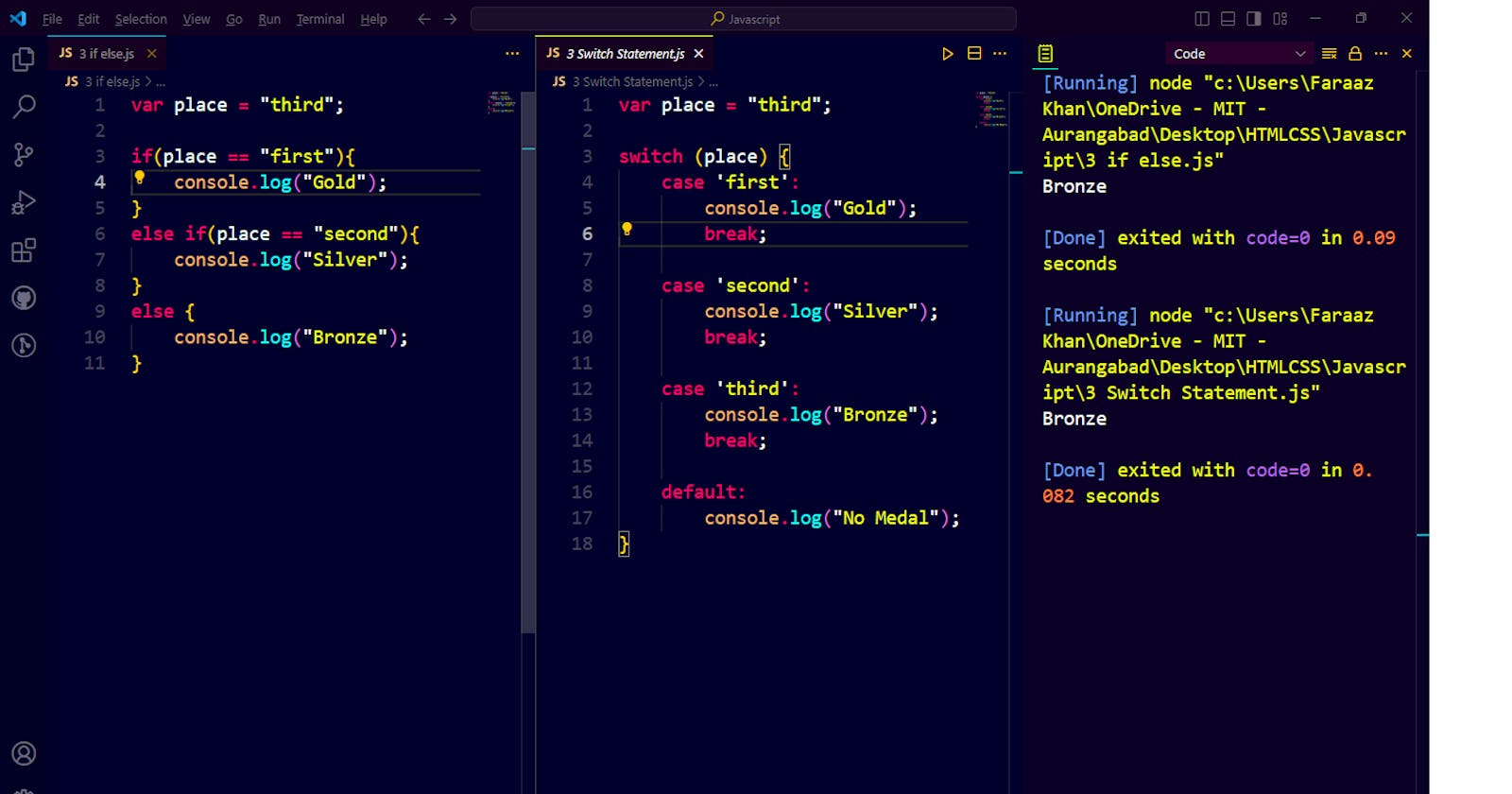
var place = "third";
if(place == "first"){
// code to run if the condition is true
console.log("Gold");
}
else if(place == "second"){
// code to run if the condition is false
console.log("Silver");
}
else {
// code to run if every condition is false
console.log("Bronze");
}
In this example:
We have a variable
placewith the value"third".The
if...elsestatement checks the value ofplaceagainst different conditions.If the first
ifcondition is true, it executes its corresponding block of code.If the first
ifcondition is false but theelse ifcondition is true, it executes theelse ifblock.If none of the conditions are true, it executes the
elseblock.
Explanation:
if (place == "first") {: Ifplaceis equal to"first", it logs"Gold".else if (place == "second") {: Ifplaceis equal to"second", it logs"Silver".else {: If none of the conditions are true (in this case, ifplaceis not"first"or"second"), it logs"Bronze".
When to Use if...else?
if...elsestatements are used when we have multiple conditions to check.They are flexible and allow us to handle various scenarios.
switch Statement
The switch statement is like choosing from a menu. It's useful when you have many different conditions to check.
var place = "third";
switch (place) {
case 'first':
console.log("Gold");
break;
case 'second':
console.log("Silver");
break;
case 'third':
console.log("Bronze");
break;
default:
console.log("No Medal");
}
In this example:
We have a variable
placewith the value"third".The
switchstatement checks the value ofplaceagainst different cases.If
placematches a case, it executes the corresponding code block.If none of the cases match, it executes the
defaultblock.
Explanation
case 'first':: Ifplaceis"first", it logs"Gold".case 'second':: Ifplaceis"second", it logs"Silver".case 'third':: Ifplaceis"third", it logs"Bronze".default:: Ifplacedoesn't match any case, it logs"No Medal".
Why Use switch?
The switch statement is handy when you have several conditions to check against a single variable. It makes the code more readable and manageable compared to long chains of if...else statements.
Conclusion
Understanding when and how to use if...else and switch statements is fundamental to writing effective JavaScript code. Whether you're making simple decisions or managing complex scenarios with multiple conditions, these statements give you the tools to control your program's flow.